Rotating Schedule: A Guide with Examples & Templates
To meet the demand of a fast-paced economy, many firms and businesses have to operate outside regular hours and even 24/7. Keeping the business open while maintaining employee wellbeing has become a challenge.
Business owners use different types of schedules to address that challenge, including a rotating schedule in which employees rotate between day shifts and night shifts (and maybe a third shift).
But what exactly is a rotating schedule and how is it different from a fixed schedule? If shift rotation is suitable for your business, then how can you create a rotating schedule that is practical?
What is a rotating schedule?
A rotating schedule is a schedule arrangement in which employees work day shifts for a period of time, then switch to night shifts for some time, and then go back to working day shifts. For some businesses, staff may rotate to a third shift. Employees keep rotating between different shift times, hence the name rotating schedule.
How does a rotating schedule work?
Imagine you run a coffee shop that opens 24/7 and runs on 3 shifts:
- First shift: 7 am – 3 pm
- Second shift: 3pm – 11 pm
- Third shift: 11 pm – 7 am
It would be simple to use a fixed schedule in which some staff will always work the first shift, some will always work the second shifts, and others will always work the third shifts.
But the problem is that night shifts are busier and bring more tips than day shifts. To make it fair for everyone, that’s where the rotating schedule comes in.
With a rotating schedule, a worker may work the first shift for 1 week, then switch to the second shift for 1 week, then switch to the third shift for 1 week. After completing the cycle, that staff will go back to working the first shift. This arrangement allows all staff to have an equal workload and equal opportunities to earn extra.
Types of rotating schedules
To accommodate the shift needs of different businesses, many variations of the rotating schedule are created. Below are the most common options.
Pitman schedule
With a Pitman shift schedule, 4 teams of employees will work 12-hour shifts and rotate their shifts every 4 weeks based on this pattern:
- 2 days on
- 2 days off
- 3 days on
- 2 days off
- 2 days on
- 3 days off
2 teams work day shifts and 2 teams work night shifts.
On any given day, 1 team works day shift, 1 team works night shift, and 2 teams are off.
This type of schedule gives your staff 3 days off every other week and they don’t have to work more than 3 days in a row. But they will have to work long shifts, which can be exhausting.

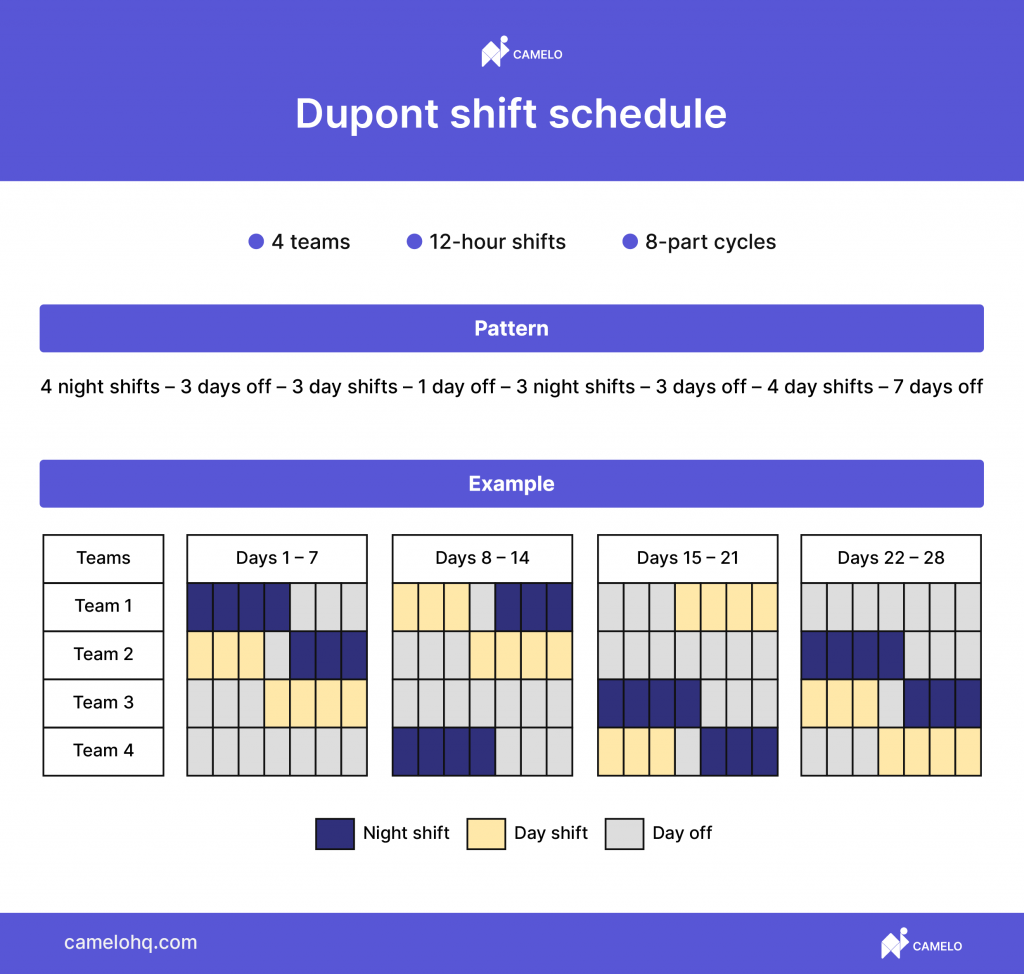
Dupont schedule
Another rotating schedule for 4 teams working 12-hour shifts is the Dupont shift schedule. Employees rotate through an 8-part cycle:
- 4 night shifts
- 3 days off
- 3 day shifts
- 1 day off
- 3 night shifts
- 3 days off
- 4 day shifts
- 7 days off
This schedule allows your staff to have a whole week off each month.
But they have to work longer hours each shift, there’s only 1-day break within the month, and it’s hard to come back to work after a long vacation. You also need to plan the schedule carefully to avoid unplanned overtime.
2-2 3-2 2-3 schedule
The 2-2, 3-2, 2-3 schedule is a common variation of the Pitman schedule. It works for 4 teams with 12-hour shifts. The cycle repeats every 2 weeks:
- 2 day shifts
- 2 days off
- 3 day shifts
- 2 days off
- 2 day shifts
- 3 days off
With this type of schedule, staff work longer shifts, but they have 3 days off every other week and don’t have to work over 3 days in a row.
But the constant switch between day and night shifts may disrupt employees’ sleep patterns because their bodies don’t have enough time to adjust.
Other variations of this schedule include: 2-2-3, 3-2-2-3, and 3-2-2.

24-48 schedule
In a 24-48 schedule, 3 teams of employees will work 24-hour shifts. The cycle repeats every 3 days: employees work for 24 hours and take 48 hours off.
Although employees only work 3 days a week and don’t have to work an entire weekend, 24-hour shifts are too long for some people. This might cause fatigue, burnout, and other safety risks. You may need to divide the team on each shift so that employees can have proper rest time.

4-3 schedule
In a 4-3 rotating schedule, 6 teams of employees will work overlapping 10-hour shifts, and the cycle repeats every 3 weeks:
- 4 days on
- 3 days off
- 4 days on
- 3 days off
- 4 days on
With this type of schedule, 3 teams will always work on weekends. But everyone has 3 days off and they work on the same days every week. You can also take advantage of the overlapping hours by scheduling them to match busy hours in your business.

Benefits of a rotating schedule
Maintains fairness
In certain industries such as Food & Beverages, night shifts are busier than day shifts. Staff working night shifts receive more tips, but their workload is heavier. A rotating schedule ensures all staff have a fair share of tips and workload. No one is stuck in slow and unprofitable shifts forever.
Increases flexibility
A rotating schedule increases flexibility in work hours and employee performance. As employees are already familiar with all shift hours, they can easily cover any shifts.
Also, a rotating schedule allows employees to schedule appointments and personal events within the weekday, 9-5 time frame. They can attend parent meetings or go to the bank without requesting a weekday off.
Gives staff more experience
A rotational schedule requires your staff to experience every hour your business opens. They can understand the ins and outs of the business and their jobs. With the experience gained from working in different situations, staff can step in when needed and don’t get lost when facing busy shifts.
Helps meet the market demand
The main purpose of a rotating schedule is to ensure coverage for the business and meet the demand of the market.
Gives employees more combined days off
As staff work longer shifts, they have more days off combined every week or month. For example, with a Dupont schedule, your staff have a whole week off, which is enough for a short vacation.
Challenges of a rotating schedule
While the benefits of a rotating schedule are obvious, it also brings many challenges to both employers and employees.
Harms work-life balance
Some employees still prefer a conventional, fixed schedule because it’s easier to maintain their work-life balance. It allows them to attend courses and schools. They can spend time with friends and family who also work conventional hours. They can sleep at the same time every day. It’s hard to maintain all those activities with a rotating schedule in which the work hours keep changing.
Involves longer shifts
Despite the attractive combined days off, longer shifts are overwhelming and exhausting to many people.
Leads to health problems
Switching between day and night shifts can mess with your staff’s natural circadian rhythm, resulting in multiple disorders and diseases. Lack of social contact due to an inconsistent schedule may lead to mental health problems.
Complicates scheduling work
Implementing a rotating schedule requires more work than a fixed schedule because you have to arrange teams into different shift hours, calculate more complex payroll, and plan for employee wellbeing.
As you can see, implementing a rotating schedule can be challenging. You should talk to your staff, see if they’re willing to work a rotating schedule and see if you can handle the scheduling work that comes with this type of schedule.
How to make a rotating schedule
Here’s a step-by-step guide to making a rotating schedule for your business:
1. Choose a type of rotating schedule
Depending on your business, industry, and staff preferences, you can choose one type of rotating schedule and adjust it to suit your scheduling strategy.
For example, you run a coffee shop with these details:
- Opening hours: 8 am – 12 am, all week
- Day shift: 8 am – 4 pm
- Night shift: 4 pm – 12 am
- Number of employees: 20
With 12-hour shifts and employees that can be divided into 4 teams, a Dupont schedule will be a good fit for your coffee shop.
Let’s say you choose the Dupont method. What’s next?
2. Divide your employees into teams
Count the total number of your employees. Then divide them into teams. Remember to include all the roles necessary for each shift. Label the teams so that you can easily arrange the shifts.
For example:
Each shift in your coffee shop requires 5 roles: a barista, a waiter/waitress, a cashier, a dishwasher, and an assistant manager.
With 20 employees, you can divide them into 4 teams of 5 people. Label each team 1, 2, 3, and 4.
3. Assign shifts to each team
Now that you’ve chosen the method and divided employees into teams, it’s time to assign shifts to each team.
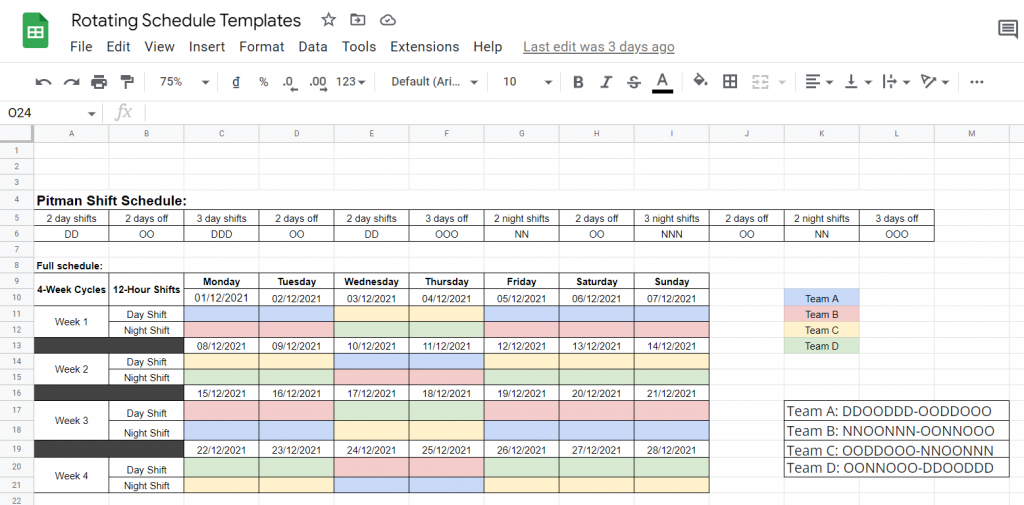
Your final schedule may look something like this:

Rotating schedule templates on Google Sheets
You can make copies of our free rotating schedule templates and adjust them to create schedules for your business.



Fixed schedule vs. rotating schedule
What is a fixed schedule?
A fixed schedule is when the employee schedule doesn’t change. One team always works day shifts, another team always works night shifts, and the third team always works wing shifts.
Why should you use a fixed schedule?
A fixed schedule is predictable and consistent. Many employees prefer this type of schedule because they can easily plan ahead appointments and personal events. It allows them to maintain a better work-life balance and better health. Employees tend to be happier, so the turnover rate is lower.
Because a fixed schedule doesn’t change much, managers don’t have to spend excessive time on employee scheduling. A flexible schedule requires lots of adjustments to make it work for everybody.
Will a rotating schedule work for your business?
Talk to your staff
Different businesses and industries may require you to adapt your schedule accordingly. However, the most important thing you need to do is to talk to your staff.
Your staff are the ones in charge of the shifts, so make sure that they’re willing and consent to follow a rotating schedule. It’s best to discuss the benefits and challenges of this type of schedule so they can decide.
But sometimes, your staff can’t always pick the perfect schedules for themselves. Sometimes, it’s the nature of the job. Without people working around the clock, the economy’s and society’s demands can’t be met. If this type of schedule is necessary for your business, you should explain and discuss the importance and implementation of it with your workforce.
Inform your future candidates
If you’ve decided to use a rotating schedule for your business, you can tell your candidates beforehand, during the interview process. This is to avoid hiring people who aren’t willing to work rotating shifts—they’re more likely to be dissatisfied and leave.
Use employee scheduling software
Implementing a rotating schedule can be difficult for both employers and employees. Managing a schedule that requires constant adjustments is no easy feat. A poorly-arranged schedule can harm your staff’s mental and physical health.
One simple way to make it easier for both is to use good employee scheduling software to create work schedules. Managers don’t have to waste too much time adjusting shifts. Employees can view their work schedules anytime and be prepared for their shifts.
Maintaining a rotating schedule isn’t hard
Without a rotating schedule, your chances of meeting the market demands are impossible. And when you create one the right way, you can quickly leapfrog your business operations.
Now you have everything you need to get started with creating a rotating schedule. Don’t forget to download our templates or try out the Camelo scheduling app, and make great schedules for your employees.







