9 Effects of Working Night Shift: How to Survive & Stay Healthy
Nearly 16% of U.S. workers work non-daytime shifts, including nights, evenings, split shifts, and irregular schedules. As we’re living in a 24-hour society with the rapid growth of consumerism, businesses are working around the clock to provide products and services.
Night shifts, taking place from about 11 p.m. to 8 a.m, are very common in many industries and occupations. But working overnight for a prolonged period of time can cause several health issues, affecting both employees and employers.
In this post, we’ll discuss 9 effects of working night shift and 28 tips for both employers and employees to handle these irregular work hours.
9 effects of working night shifts on workers’ health
1. Disrupts your sleep-wake rhythm
While you sleep, the internal processes in your body work to help your body rest, repair injuries, and eliminate toxins. Working night shift interferes with these processes and lead to several health risks.
2. Cuts production of melatonin
Night shift work is associated with the suppression of melatonin production. Humans sleep better when melatonin is secreted. Reduced melatonin levels are linked with various diseases such as diabetes, cancer, mood disorders, etc.
3. Increases risk of heart problems
Women working rotating night shift work had an increased risk of coronary heart disease. AFib, an irregular heart rhythm that can result in strokes, was also linked to long-term night shift work.
4. Increases risk of obesity and diabetes
Changing your sleep pattern causes hormonal imbalance that leads to obesity and diabetes. Night workers also consume more night-time snacks and processed foods, which adds up to these health risks.
5. Knocks your gut out of sync
Our digestive system has its own biological clock, and working night shifts knocks the gut out of sync. People on night shifts may suffer stomach pains and gut problems such as ulcers or diarrhea.
6. Increases risk of breast cancer in women
Studies show that night shift work is a big risk factor for breast cancer, especially for women working night shifts for a prolonged time. People working nights are exposed to more artificial light and make less melatonin, a hormone that helps prevent tumor growth.
7. Leads to mental health issues
Night work certainly takes a toll on workers’ mental health. Night shifts disrupt the natural sleep cycle, making people irritable and moody. Working nights also makes it hard for workers to spend time with family, friends, and other life commitments, which leads to social isolation.
8. Lacks vitamin D
Vitamin D deficiency causes various diseases and disorders such as breast cancer, heart diseases, depression, etc. Night workers are exposed to less sunlight—the main source of vitamin D for humans.
9. Increases risk of injury
Working at night disrupts the natural circadian rhythms of human bodies, resulting in reduced attention, productivity, and reaction to unexpected situations. Workers’ judgment and motor skills are also lower at night. Some may even doze off on their shifts, which can be dangerous if they’re working with machines.

6 disadvantages of night shifts: what employers need to prepare
1. Bigger health costs
Despite the profitable and productive side of night shifts, working at non-daytime hours can take a toll on your employees’ health. Roughly 10% of people who work night shifts and rotating shifts have a shift-work sleep disorder. A company may have to pay over $3,200 a year for the health costs of each employee with sleep deprivation.
2. More supervision required
The lack of management at night can affect the productivity and the safety of employees. This means managers need to be present at night to supervise their staff or find someone else to do so.
3. Criminals
Businesses operating at night often face the threats of criminals, so managers need to consider hiring safeguards and installing security systems to prevent burglars, vandals, and thieves.
4. More scheduling work
To keep your employees awake and alert, you have to plan more breaks for workers, as compared to day-time shifts.
5. Not appealing to job seekers
Night shift jobs are less appealing to job seekers because people are well aware of the consequences of night shifts.
6. Workplace injuries and errors
A study has shown that the risks of injuries and errors in night shifts are 28% higher compared to day shifts. You need to take more measures to ensure the performance and safety of workers.
How to work the night shift and stay healthy: 18 tips for night shift workers
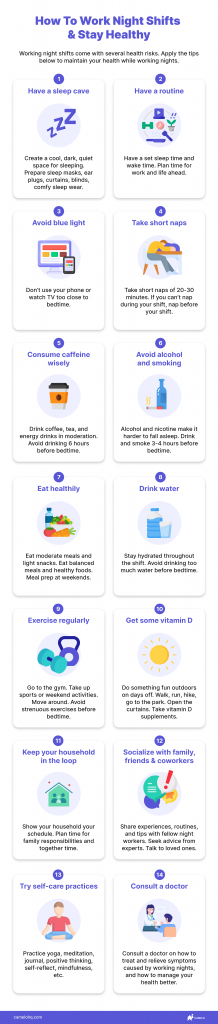
1. Have a sleep cave
Having a good night’s sleep is a big part of staying healthy while working overnight. That’s why you need a sleep cave.
Your sleep cave should be cool, dark, and quiet to help you fall asleep easier and sleep deeper.
If you’re sensitive to lights, use sleep masks, curtains, and blinds. If you can’t wake up in the dark, try a wake-up light. It gradually increases the light in your room before your wake time.
If you’re sensitive to sounds, use earplugs.
Oh, and don’t forget to wear cool and comfy sleepwear.
2. Regulate temperature for sleep
To sleep comfortably, it’s suggested to keep your room temperature at around 65 degrees. But everyone is different, so experiment to find what temperature suits you best.
You may want to turn down the thermostat when you sleep, use a blanket to keep you warm, or turn on the fan during warmer daytime.
3. Avoid blue light before bedtime
The blue light coming from screens affect the production of sleep hormones, making it harder to fall asleep and disrupting your sleep quality.
It’s very tempting to watch TV or scroll on your phone before bedtime, but you should avoid screens if you want to get a restful sleep.
4. Have a routine
Set up a routine with planned time for sleep, work, and life. Sticking to a set sleep and wake time helps your body prepare for night shifts. Having a plan makes sure you spend time on important things in your life.
5. Take short naps
Short naps help you recharge energy during a long night shift.
Short naps of about 20-30 minutes are ideal. Longer naps get you into a deep sleep state and make you groggy when you wake up.
If your workplace doesn’t allow naps within the shift, you can nap before your shift.
6. Consume caffeine wisely
Most people working night shifts drink coffee, tea, or energy drinks to stay awake and fulfill their responsibilities throughout the night.
Caffeine stays in your body for hours, so drinking it too much and too close to bedtime may affect your sleep quality.
Drink in moderation. The best time to drink is before your shift and 6 hours before your bedtime.
7. Avoid alcohol
Drinking alcohol before bed affects your sleep quality and interrupts your sleep-wake rhythm. Although it may make you fall asleep easier, you may feel tired and drowsy when you wake up.
8. Avoid smoking
Smoking makes you feel relaxed, but nicotine actually makes it more difficult to fall asleep. If you’re a smoker, it’s suggested to do so 3-4 hours before going to bed.
9. Eat healthily
Since night work comes with lots of health risks, diet should be an important part of your lifestyle.
Instead of having a giant meal before your shift, try eating a moderate meal and having small snacks throughout the night. Big meals make you sluggish and put pressure on your digestive system.
Since working nights messes up your digestive system, be thoughtful about what to eat and what not. Prep meals with a balanced amount of carbs, protein, and fat. Avoid processed foods and fast food. Snack on salads, veggies, fruits, and trail mix instead of sugary foods.
Besides being selective about what to eat, when to eat is also important. Ideally, you’ll want to eat a moderate meal before the night shift, snack lightly throughout the night, and have a light breakfast before you go to bed.
10. Meal prep and meal delivery service
If you have problems thinking of what to eat and finding the time to cook, meal prep at weekends can be a great idea. It’s cheaper and you can control what you consume. There are plenty of recipes and ideas online.
If you can’t find the time or the energy to prep your food, try a meal delivery service that offers healthy dishes instead of going for fast food and vending machines.
11. Drink water
Keeping your body hydrated keeps you alert and energized. Sip water throughout your shift, but avoid drinking too much before bedtime.
12. Stay active
Moving around keeps you alert and your blood flowing. If your work allows, try to walk around and stretch instead of just sitting.
13. Exercise regularly
Exercising regularly helps you increase the strength and energy to work night shifts.
Get your heart rate up with intensive gym sessions. Incorporate exercise with weekend activities such as hiking or cycling.
If your workload is too heavy, finding the motivation to exercise can be hard. To keep yourself accountable, find workout friends, work out with a personal trainer, or pay for classes. Put activewear and shoes out the day before so you have no excuse not to work out.
If you work out after your shift, avoid strenuous exercises because they may make falling asleep more difficult.
14. Get some vitamin D
Vitamin D deficiency is common among night workers because they sleep when the sun comes up. Lack of vitamin D affects your calcium levels and bone health.
On days when you’re not working, get some sunlight to absorb the vitamin D that your body needs. Walk, run, hike, or go to the park. Open your curtains. Do something fun outdoors. Or take vitamin D supplements.
15. Keep your household in the loop
If you work irregular hours, show your household your work schedule. This lets people know when you sleep so they can avoid interrupting you. Knowing when you work also helps with planning time for childcare, family responsibilities, and time for each other.
Socialize with your night coworkers to keep you from nodding off. Find communities where fellow night workers or professionals share experiences, routines, habits, and tips to better survive the night shifts. Talk to friends and family about your concerns and seek their advice.
17. Try self-care practices
Working long, tiring hours and having little time for social interactions, night workers are prone to stress and other mental health issues. Try adopting self-care practices such as yoga, meditation, journal, positive thinking, self-reflect, etc.
18. Consult a doctor
If symptoms from working night shifts such as insomnia or headaches persist, you should consult a doctor on how to treat and relieve them, as well as how to manage your health better.
Tips for employers on how to manage night shifts
19. Find out what your staff prefer
Even though night work seems to be universally hated, some people actually enjoy working nights. Ask about your employee preferences and take those into account when scheduling them.
20. Talk about night shift work
Talk to your employees about the quality of sleep, sleep-related problems and solutions, night work risks, tips to stay healthy, and sources they can come to for support.
Encourage your staff to have regular physical exams and seek help when they’re in need. Let workers know that you care about them, not just how much they can do for you.
21. Allow naps
Let your staff take short naps and recharge their energy. You can apply rotating breaks where groups of night workers take turns to take breaks. That way there’ll always be someone on shift while others rest.
22. Redesign the work environment
The work environment of night workers should be designed to best support night work.
Provide good lighting, ventilation, nap rooms, and even anti-fatigue rubber mats if you have standing employees.
Provide a cafeteria where night workers can get proper, balanced meals before their shifts. Have a pantry filled with healthy snacks and beverages so workers can munch when they’re hungry.
Invest in safety measures and equipment to protect employees and avoid unexpected accidents that may affect your business reputation.
23. Provide wellness programs, classes, and resources
To help night employees, employers should provide programs, classes, workshops, and resources on wellness, stress management, and how to cope with night shifts better.
24. Have someone supervise night shift workers
Night workers are prone to accidents and mistakes due to less supervision from management at night. They’re also more likely to suffer from disorders and diseases. A shift manager should be on site to identify those who struggle and support them at the right time.
25. Offer attractive perks
Night shift jobs appear to be less attractive, so you can offer more appealing perks such as a higher wage, daycare solutions, and transportation to attract talented and competent workers.
26. Provide annual health checks
Annual health checks help your staff identify health problems early on and take measures before their health and productivity go downhill.
27. Create a predictable and well-planned work schedule
Predictable and well-planned work schedules help employees cope with night shifts better. Employees have enough time for meals, sleep, and breaks. Long shifts have more breaks. Demanding tasks are scheduled earlier in the shift. Schedule changes are notified early so workers have enough time to adjust their sleep patterns.
Taking employee needs into account while scheduling may seem like a lot of work. But it’s not impossible. And with the help of free scheduling apps like Camelo, you can easily create work schedules that are considerate and effective. Try it free today.






